What is cancer?
Cancer is a term used for disorders in which abnormal cells split without control and can attack other tissues. Cancer cells can grow to other parts of the body by the blood and lymph ways. Cancer is not just one disorder but many disorders. There are more than 100 Types of Cancer Treatment. Other official terms used are cancerous tumors and neoplasms. Cancer can attack around any part of the body and has many anatomic and molecular subtypes that each need specific management plans.
Cancer is the second chief reason of death globally and is expected to consider for 9.6 million death in 2018. Prostate, colorectal, lung, stomach, and liver cancer are the most basic kinds of cancer in men, while Cervix, breast, colorectal, lung, and thyroid cancer are the most prevalent amongst women.
Differences between Cancer Cells and Normal Cells
Cancer cells vary from healthy cells in various behaviors that allow them to develop out of control and grow invasive. One major variation is that cancer cells are less functional than normal cells. That is, whereas normal cells mature into very different cell types with special functions, cancer cells do not. This is one object that, unlike normal cells, cancer cells proceed to divide without end.
Cancer cells may be capable of changing the normal cells, molecules, and blood veins that surround and support a tumor a field known as the microenvironment. For example, cancer cells can cause nearby healthy cells to form blood vessels that provide tumors with oxygen and nutrients, which they require to develop. These blood vessels also discard waste products from tumors.
How does cancer spread?
Cancer that has grown from the place where it first began to a different place in the body is called metastatic cancer. The manner by which cancer cells grown to other portions of the body is called metastasis.
Metastatic cancer has an equal name and the same kind of cancer cells as the original, or primary, cancer. For case, breast cancer that grows to and makes a metastatic tumor in the lung is metastatic breast cancer, not lung cancer.
What Causes Cancer to Develop?
Cancer starts in the cells, which are the primary building blocks, that makeup tissue. The tissue is located in the breast and other parts of the body. Sometimes, the method of cell increase goes incorrect, and new cells develop when the body doesn’t require them, and old or injured cells do not vanish as they should. When this happens, a build-up of cells usually forms a portion of tissue called a lump, thickening, or tumor. Breast cancer happens when cancerous tumors develop in the breast. These cells can increase by splitting away from the first tumor and entering blood vessels or lymph veins, which branch into tissues everywhere the body.
Symptoms of Cancer
Cancer provides most people with no signs or symptoms that mainly show the disease. Sadly, every illness or symptom of cancer can be defined by a simple condition as well. If specific manifestations happen or continue, however, a doctor should be consulted for additional evaluation. Some primary symptoms that may appear with cancer are as follows:
- Breast changes
- Bladder changes
- Bleeding or bruising
- Blood in the stools
- Cough or hoarseness that does not go away
- Appetite changes
- Fatigue that is severe and lasts
- Fever or night sweats
- Neurological problems
- Skin changes
- Swelling or lumps
- Weight gain or weight loss for no known reason
Causes of cancer
There is no appropriate cause for cancer. Experts conclude that it is the cooperation of many circumstances collectively that creates cancer. The factors involved may be genetic, environmental, or inherent.
Cancer is created by grown damage to genes. Such modifications may be due to coincidence or to exposure to cancer, causing substance. The things that cause cancer are called carcinogens. A carcinogen may be a chemical material, like particular particles in tobacco smoke. The cause of cancer may be environmental factors, viral or biogenetic parts.
Cancer Risk Factors
Lifestyle parts: Smoking, a high-fat diet, and operating with poisonous chemicals are parts of lifestyle options that may be risk factors for some adult cancers.
Family records: Inheritance and heredity may play an essential role in some babyhood cancers. It is reasonable for cancer of different forms to be present more than once in a family. It is unexplored in these conditions if the disorder is caused by a genetic change, exposure to chemicals near a family’s residence, a mixture of these parts, or simply chance.
Some genetic diseases: Like, Wiskott-Aldrich and Beckwith-Wiedemann symptoms are known to change the immune system. The immune system is a complicated system that operates to defend our bodies from disease and illness.
Exposures to some viruses: Epstein-Barr virus and HIV, the virus that produces AIDS, linked to an enhanced opportunity of developing some childhood cancers, such as Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Probably, the virus changes a cell in an unusual route.
Environmental exposures: Pesticides, fertilizers, and power lines have been studied for a direct link to minority cancers. There has been proof of cancer happening amongst nonrelated children in some communities or cities.
Some applications of high dose chemotherapy and radiation: In some matters, children who have been presented to these agents may develop a second virulence later in life.
Types of Cancer Treatment
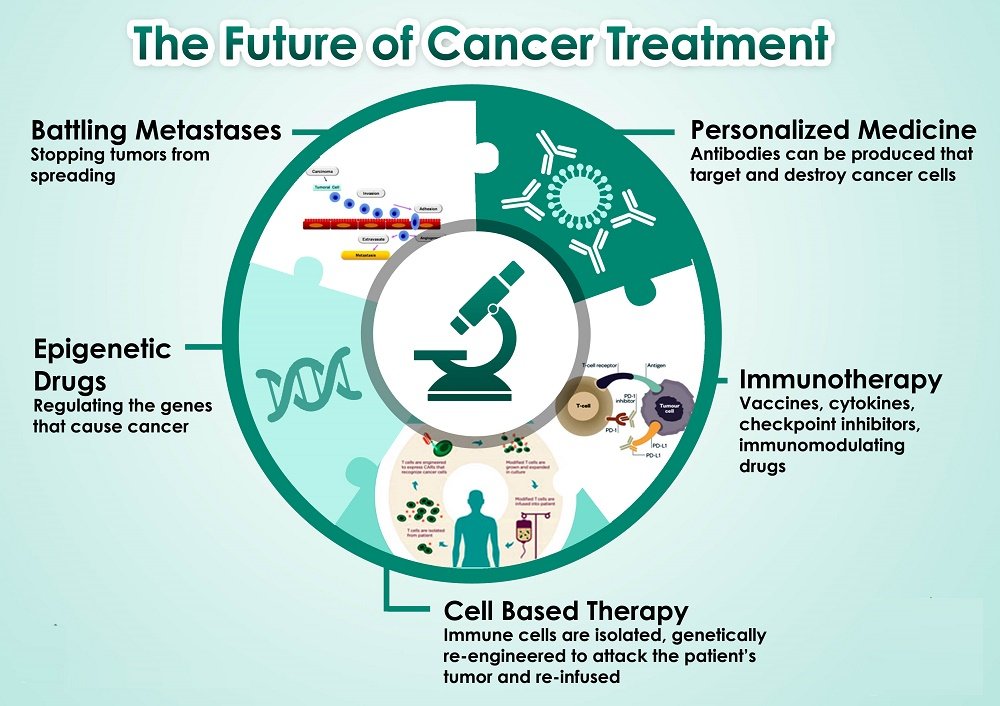
It’s necessary to read about all your treatment choices to make the choice that is best for your condition.
Look out what you want to know about the most current types of cancer treatment, such as surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. Learn as much as you can regarding how they work and what to suppose if they are part of your treatment program.
Common Treatments for Cancer
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation Therapy
- Targeted Therapy
- Immunotherapy
Other Procedures and Techniques
- Stem Cell Transplant
- Hyperthermia
- Photodynamic Therapy
- Blood Transfusion and Donation
- Lasers in Cancer Treatment
Types of Cancer
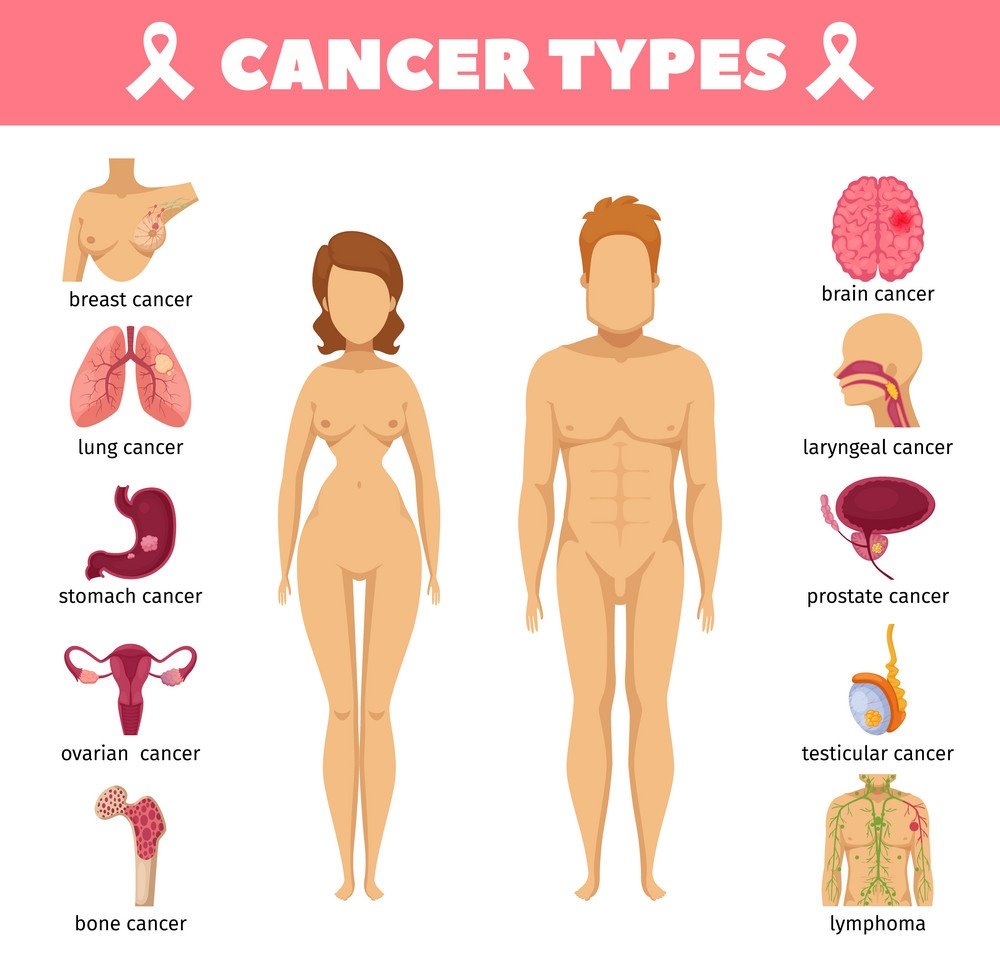
| Bladder Cancer | Breast Cancer | Cervical Cancer |
| Colorectal Cancer | Gynecologic Cancers | Head and Neck Cancers |
| Kidney Cancer | Liver Cancer | Lung Cancer |
| Thyroid Cancer | Uterine Cancer | Vaginal and Vulvar Cancers |
| Ovarian Cancer | Prostate Cancer | Skin Cancer |


































[…] four major types of cancer are carcinoma, sarcoma, lymphoma, and […]
Comments are closed.