What happens if you have an ectopic pregnancy?
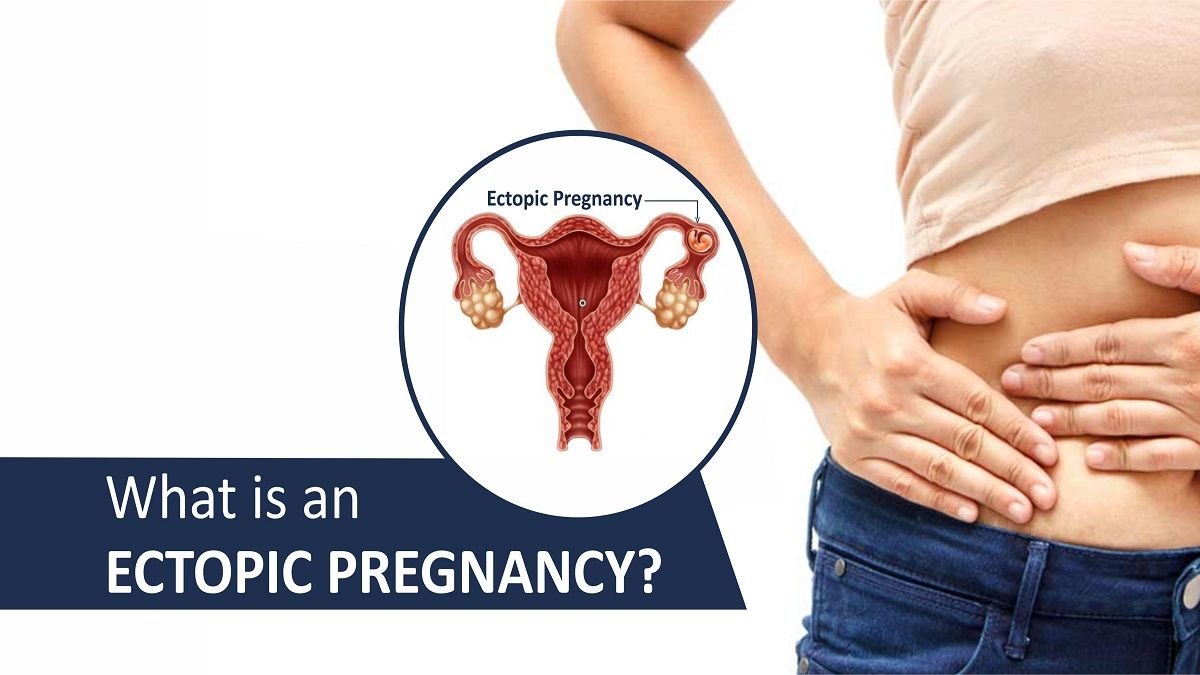
In a healthy pregnancy, an impregnated egg travels through a fallopian tube to the womb. The egg attaches to the womb and begins growing. But in an ectopic pregnancy (also known as an extrauterine pregnancy), a fertilized egg implants in another place but not the womb, frequently in a fallopian tube.
An ectopic pregnancy is often caused by damage to the fallopian tubes. An impregnated egg can have difficulty in traveling through a damaged tube, causing the egg to attach and grow in the tube. Rarely, the egg implants in an ovary, the cervix or the belly. If the egg keeps growing in the damaged fallopian tube, it can damage or burst the tube and lead to heavy bleeding that could be lethal. If you think you have an extrauterine pregnancy, you need prompt treatment to stop it before it leads to severe health problems.
Factors bringing on salpinges damage
- Smoking. The more cigarettes a day you smoke, the higher your risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). This is often the resolution of an infection such as chlamydia or gonorrhea.
- Endometroid heterotopia, which can cause scar tissue in or around the uterine tubes.
- A history of repeated induced terminations of pregnancy.
- You are being exposed to the chemical DES before birth.
Ectopic Pregnancy Symptoms
Pain is commonly the first symptom of an ectopic pregnancy. The pain, often one-sided, maybe in the pelvis, abdomen or even in the shoulder or neck. The pain usually is excruciating. Weakness, light-headed, or fainting can signal severe internal hemorrhage, requiring immediate medical aid.
Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosis
Diagnosis of an extrauterine pregnancy includes an ultrasound, a pelvic examination administered to test for pain, tenderness, or a mass in the abdomen. The most useful lab test is the measurement of the hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin).
Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
Treatment of an extrauterine pregnancy is surgery, frequently by laparoscopy these days, to remove the ectopic pregnancy. A ruptured Oviduct usually has to be removed. If the tube has not ruptured yet, it may be possible to fix it.
Future pregnancies
The extent of the operation impacts the chance of successful future pregnancies. If the Oviduct has been fixed, the chance of a successful pregnancy is commonly higher than 50%. If a uterine tube has been excised, an egg can be fertilized in the other tube, and the probability of a successful pregnancy is lower than 50%.












One thought on “What is an ectopic pregnancy? Symptoms & Treatment”
Comments are closed.