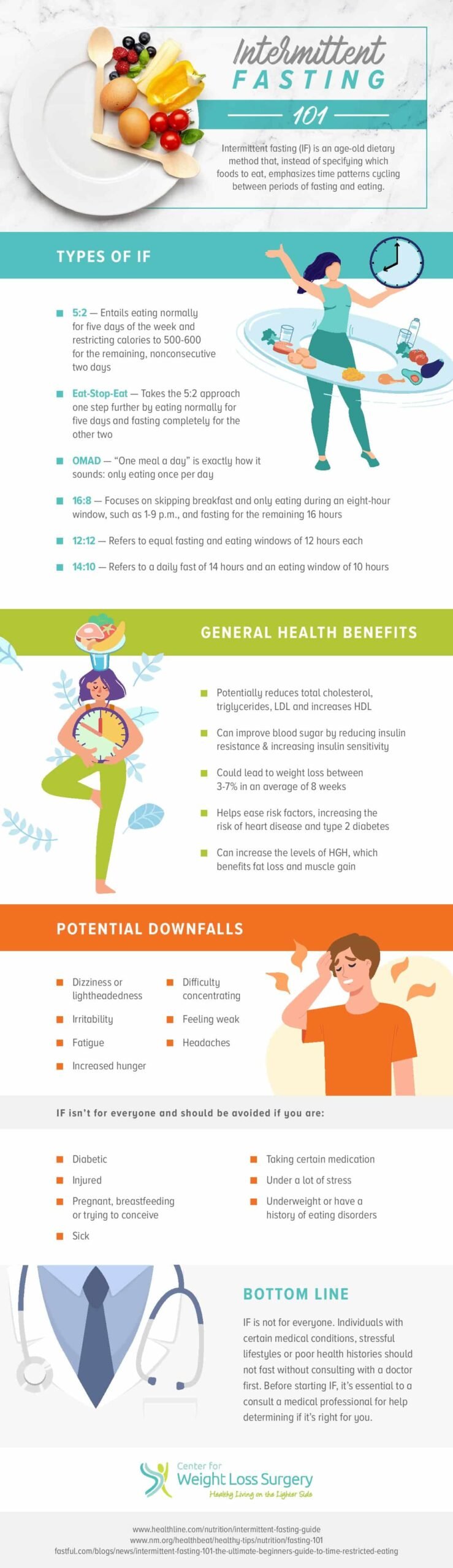
Intermittent fasting (IF) is far more than another diet fad. Studies show that an intermittent fasting eating plan, which limits food and drink consumption to specific times of day, may offer numerous mental and physical health benefits. Learn more about intermittent fasting and how it may help improve your overall wellness here.
What Is Intermittent Fasting?
People around the globe have been fasting for cultural, religious, and health reasons for thousands of years. However, intermittent fasting became popular in 2012, when BBC journalist Dr. Michael Mosley released his book “The Fast Diet” and documentary “Eat Fast, Live Longer.” Several other bestselling books were released shortly after, generating interest in intermittent fasting and its health benefits.
Intermittent fasting is an eating plan that involves not eating for a set amount of time each day or on certain days of the week. There are several different intermittent fasting methods, but they all involve set periods for eating and fasting.
How Does It Work?
Experts like Mark Mattson, a Johns Hopkins neuroscientist who has spent 25 years studying intermittent fasting, say that prolonged periods without food cause the body to burn through sugar stores. The body switches to metabolizing fat when there’s no sugar left to metabolize.
A typical American eating pattern involves eating three meals per day, with snacks dispersed throughout. Mattson explained that the goal of intermittent fasting is for the body to consume the calories acquired during the set eating period, then begin burning fat when those calories are no longer available.
Types of Intermittent Fasting
There are several approaches people take to intermittent fasting. The most common are the 5:2, 16/8, alternate-day and eat-stop-eat methods.
5:2 Fasting
The 5:2 approach is when the person fasting eats regularly for five days per week, then limits him- or herself to one small meal on the other two days. The meal usually consists of 500 to 600 calories.
16/8 Fasting
This style of fasting involves eating during an eight-hour period each day and fasting for 16 hours. The individual chooses his or her own eating and fasting periods, but an example would be eating between the hours of 10 a.m. and 6 p.m. each day and fasting the rest of the time.
Alternate-Day Fasting
Alternate-day fasting is just as it sounds. The person eats a normal diet one day, then fasts completely or consumes one small meal the next day. If consumed, the small meal is less than 500 calories.
Eat-Stop-Eat Fasting
This fasting method is when the individual fasts for 24 hours once or twice per week. For example, he or she may eat breakfast one day, then not eat again until breakfast the next day.
Health Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
Numerous studies show the possible health benefits of intermittent fasting, ranging from weight loss to superior brain health.
Weight Loss
Intermittent fasting is often praised as a weight loss tool. Studies show evidence that alternate-day fasting could be as effective for weight loss as a low-calorie diet. Generally, methods of intermittent fasting involve eating fewer meals, less often, which reduces the number of calories a person intakes.
A 2014 study showed that intermittent fasting can result in 3% to 8% weight loss over three to 24 weeks. The same study reported that fasting individuals lost 4% to 7% of their waist circumference. The waist is a common area for fat to gather around organs, which can lead to numerous health complications.
Superior Heart Health
Research states that intermittent fasting may help lower blood sugar, inflammatory markers, bad cholesterol, insulin resistance and other factors that can lead to heart disease. Weight loss due to intermittent fasting may lead an individual to a more physically active lifestyle, further improving cardiovascular health.
Reduced Inflammation
Studies on intermittent fasting show a possible reduction of inflammatory markers. Inflammation is a driving factor in many chronic diseases and other health concerns, such as asthma, multiple sclerosis, arthritis, Alzheimer’s disease and more.
Improved Brain Health
Studies show that intermittent fasting can boost verbal memory in humans. Research also shows increases in the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) brain hormone that aids neuronal growth and survival. Intermittent fasting may help prevent Alzheimer’s disease.
Numerous studies display the possible health benefits of intermittent fasting, including anti-aging benefits, improved physical performance, tissue health and obesity prevention.
Is Intermittent Fasting for Everyone?
Many doctors, scientists and researchers believe intermittent fasting can offer numerous health benefits, but it’s not a lifestyle for everyone. Anyone considering intermittent fasting should discuss their plan with a doctor first, especially if they’re using IF for weight loss or alongside different types of weight loss surgery.
Intermittent fasting is generally not recommended for anyone with type 1 diabetes, an eating disorder or other medical conditions. Pregnant or breastfeeding women and kids or teens under 18 should not try intermittent fasting.
Common side effects include fatigue, hunger, insomnia, headaches and nausea. However, they usually subside within a month of beginning an IF regimen.
Research shows intermittent fasting may be an effective way to manage weight, improve overall health and prevent some diseases. It can also simplify a person’s lifestyle by helping control food and drink consumption. Learn more about the types of intermittent fasting, as well as their benefits and side effects, in the accompanying resource.